7 Key Factors That Impact Online Retail Gross Margin
7 Key Factors That Impact Online Retail Gross Margin
Gross margin is an indicator of how well the c-suite manages a company. Online retailers have to manage their gross margins just like traditional retailers, which involves the interaction of revenue versus the cost of goods sold.
What are the factors that most impact online retail gross margin? There are seven primary factors, and online retailers must pay attention to them.
Key Takeaways
- Gross margins for online retailers are trending upward
- Revenues and cost of goods sold both impact gross margin
- Some of the revenue-related factors that impact gross margin include sales volume, selling price, and product mix
- Factors that impact the cost of goods sold include materials, labor, and shipping costs
Online Retail Revenues are Exploding
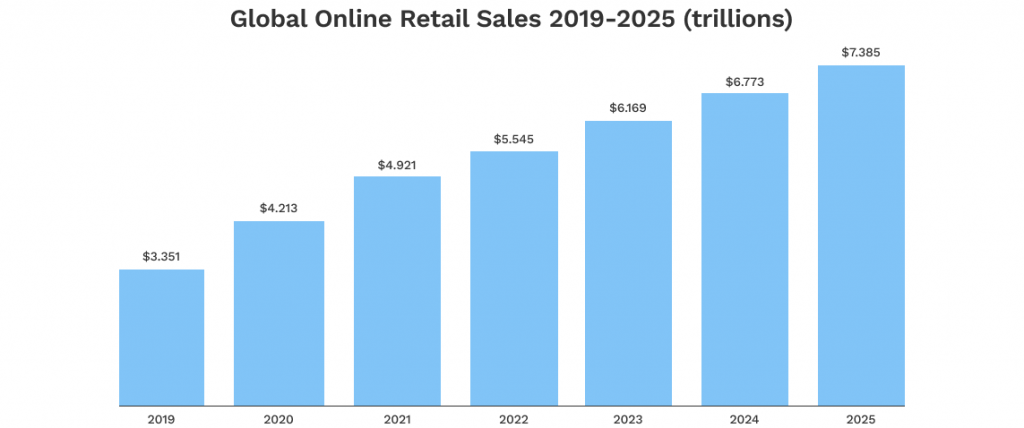
An increasing number of consumers are shopping online. More online shoppers are resulting in an explosion in online revenue, expected to surpass $7 trillion worldwide by 2025. According to eMarketer, online sales will increase by 24.5% of total retail sales within the next three years.
How profitable are online sales compared to traditional retail sales? To optimize profits, online retailers must focus on gross margin.
Online Retail Gross Margin is Trending Higher
Gross margin is calculated by dividing gross profit (gross revenue minus cost of goods sold) by gross revenue. A higher gross margin leaves more gross profit to pay for operating expenses, including payroll, rent, and marketing. A lower gross margin typically results in lower net profits for a company.
The good news is that gross margins for online retailers are trending higher. According to CSIMarket, gross margins for the internet, mail order, and online shops categories hit 41.3% in Q3 of 2022, up from 40.5% the year prior—and 39.1% in Q3 2020. The trendline for this category has been on a definite upward trajectory from the beginning of 2020 to today.
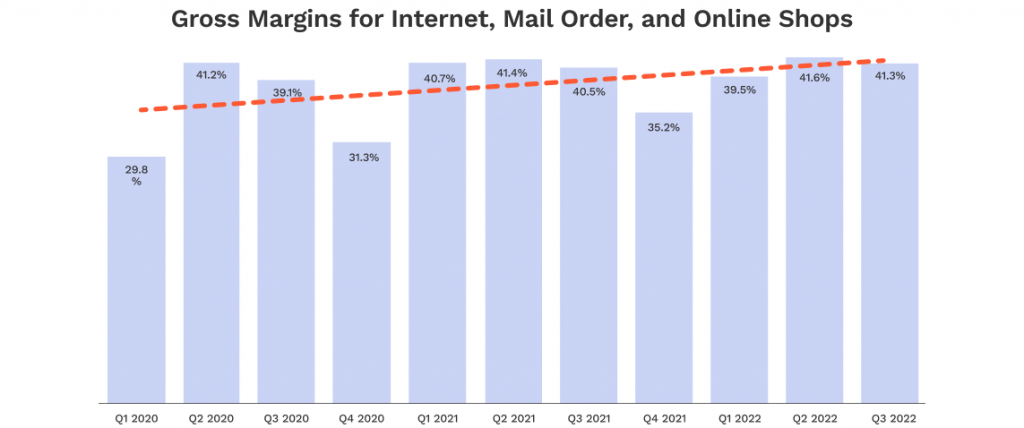
Why are online retail gross margins on the rise? There are several probable reasons:
- The ongoing recovery from the COVID pandemic, which depressed both consumer demand and margins in many sectors, is fueling higher sales
- Continuing inflation is providing cover for retailers in many sectors to increase prices
- Easing COVID-related supply chain issues are finally reducing shipping and transportation costs (Freightos reports that the cost of shipping a 40-foot container from Asia has dropped by more than 80% since just April)
- Shifting consumer buying habits are resulting in a higher-margin product mix in some sectors
- The post-COVID shakeout is reducing competition for many retailers
Will gross margins for online retailers continue to inch upward? It depends on the many factors that impact gross margin.
What Affects Gross Margin in Retail?
What factors affect gross margin? The simple view is that gross margin is affected by only two things: revenue and cost of goods sold (COGS). The more complex reality is that multiple factors contribute to revenue and COGS and, thus, to gross margin.
On what factors should your business focus on to improve gross margins? There are seven that have the biggest impact.
Sales Volume
An increase in sales can result in a higher gross margin, especially if a company has fixed product costs. As the economy improves, sales volume should increase in many sectors, thus improving gross margins.
Selling Price
Increasing sales volume isn’t a panacea for higher gross margins, however. If a product’s selling price decreases—because of promotions, discounts, and response to competition—a company could sell more units for less money. That would result in a lower gross margin.
Companies often face the temptation to slash prices to increase sales. Reducing prices can result in both unit and dollar sales increases but at the expense of gross margin. Conversely, insisting on higher prices at the expense of unit sales while increasing gross margin could result in lower revenue, jeopardizing net profit.
Product Mix
Revenue isn’t just about how much product you sell. It’s about what product you sell. A shift in product mix towards higher-priced, higher-margin products can positively impact gross margin. Likewise, if consumers start buying more lower-priced, lower-margin goods, as is happening in some segments in response to inflation, gross margin can suffer. Savvy online retailers strive for a product mix that maximizes revenue and margin.

Materials Costs
Managing inventory costs and controlling the cost of goods sold are critical elements of managing gross margin. Everything else (especially selling price) being equal, when COGS goes up, gross margins go down—and vice versa.
COGS has three primary components: materials cost, labor costs, and shipping costs. Changes in any of these three components can affect COGS and gross margin.
For many companies, the largest component of COGS is materials. If suppliers increase the cost of raw and component materials, COGS goes up—and many things can cause those materials’ costs to increase. Some factors, weather and political unrest, are beyond suppliers’ control. Businesses can try sourcing from different suppliers (sometimes with success), but managing materials cost is crucial for keeping gross margin under control.
Labor Costs
The labor used to manufacture products is also a major component of COGS. Manufacturers have done a good job over the past few decades sourcing labor to low-cost countries, but eventually, they run out of even lower-cost countries to move to. Worker unrest and political issues can have an unexpected effect on labor costs. Automating manufacturing can help mitigate labor issues, but companies can’t remove the human element from all product manufacturing.
Shipping Costs
The final component of COGS is the cost of shipping products to the retailer. This cost can be high, especially for goods manufactured overseas. Recent supply chain disruptions showed how changes in shipping could impact the final COGS.
Competition
The final factor that affects retail gross margin is competition. Stiff competition can drive prices—and gross margins—down. Competition can also negatively affect your sales, affecting how much product you manufacture, resulting in fewer bulk deals and higher COGS. No business is alone in the marketplace, and every retail aspect depends on what the competition does.
Let Hypersonix Maximize Your Gross Margin
Hypersonix is a leading provider of retail intelligence and profit optimization software. Our AI-based solutions improve demand forecasting, inventory management, and other key business functions that improve gross margin and net profit. We utilize 11 AI engines that provide the predictive and prescriptive analysis necessary to drive your business to new heights.
Contact us today for a free demo!





