How AI Is Constantly Transforming the Retail Industry
How AI Is Constantly Transforming the Retail Industry
In 2021, businesses spent an estimated $2.9 billion on products providing AI to the retail industry. With a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 34.1%, the global market for AI-driven retail technology will expand to $17 billion by Q4 of 2028.
Many emerging applications currently fuel the rapid growth of AI in retail and eCommerce. These include:
- Need for inventory intelligence
- Supply chain optimization
- Omnichannel retail marketing
- Opportunities to improve monitoring and surveillance at brick-and-mortar stores
This guide explores how AI is transforming the retail industry and the benefits businesses are reaping from implementing AI in different stages of their operations.
Key Takeaways
- Retail and ecommerce spending on AI technologies is on the rise.
- Emerging AI applications in retail are enabling real-time, data-backed decision-making in a broad range of critical operations.
- With the ability to optimize supply chains, staffing, pricing, and various aspects of customer experience, retailers who integrate AI into their operations and decision-making processes have a multipoint advantage over organizations relying on spreadsheet analytics and guesswork.
7 Ways AI Is Transforming Retail Operations
Emerging AI applications are changing the retail and ecommerce industry in several remarkable ways.
1. Enhanced Employee Performance and Productivity
In 2021, 56% of office workers reported already using AI systems in their day-to-day tasks. Of these, 81% stated that AI improved their abilities to do their jobs, and 89% estimated that additional AI adoption could support half their workloads.
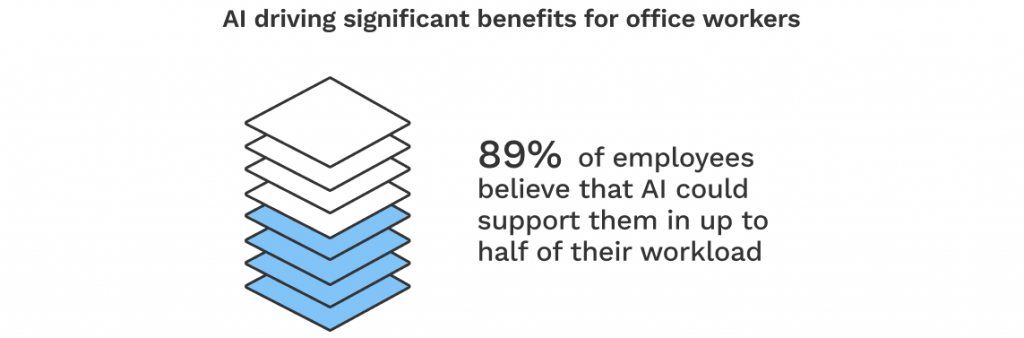
For typical office jobs, the most commonly reported uses of AI were:
- Data analytics, data visualization, and pattern recognition to drive decision-making
- Data migration between IT systems
- Aggregating data from siloed databases and applications
2. Demand Forecasting
For a diverse range of business needs such as capital-expenditure planning, risk mitigation, and workforce provisioning, demand forecasting has become a critical capability. However, the volume of relevant data that businesses must analyze to plug real values into forecasts has grown far beyond what human analysts can take in.
In place of human analysts and traditional spreadsheet-based analytical processes, cutting-edge AIs and machine learning algorithms are increasingly handling demand analytics and delivering some significant bottom-line benefits, such as reductions in:
- Supply chain management errors by 20-50%
- Lost sales and product unavailability by 65%
- Warehousing costs by 5-10%
- Administrative costs by 25-40%
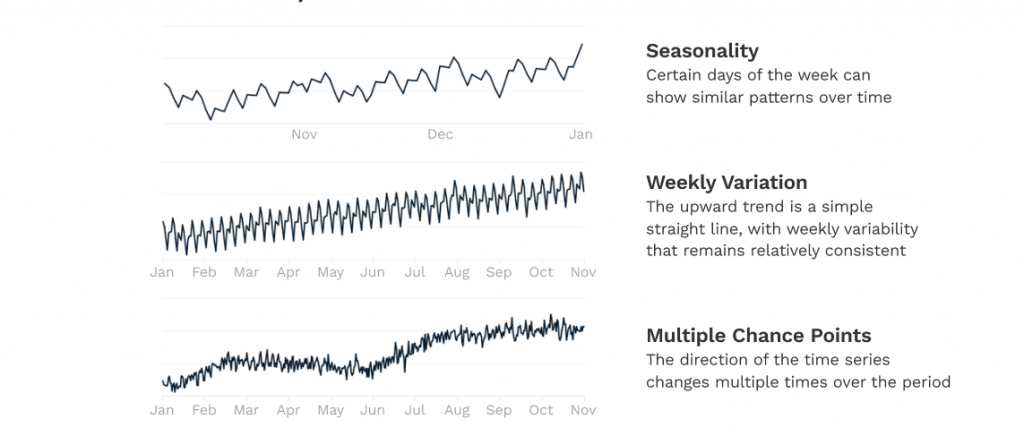
AIs accomplish better demand predictions by identifying patterns at various scales throughout a business’s historical data. Patterns with demand applications include:
- Seasonality: Repetition in values for the same weekdays, months, or seasons across multiple years
- Weekly Variation: Upward or downward linear trends
- Multiple Change Points: Unpredictable variations following external events
3. Improved Customer Satisfaction
Retailers and ecommerce businesses have been leveraging AI technology to improve customer experiences and drive overall satisfaction for nearly a decade now. Nevertheless, possibilities for new applications in this area continue to emerge.
AI enhancements for customer shopping experiences began with automated checkouts to save time, product recommendations based on past purchases in ecommerce, personalized discounts, and 24/7 customer service options through chatbots.
Today, AIs are poised to play even greater roles at each of these customer touchpoints. Computer vision technology has enabled checkout-free shopping systems that associate product purchases with customers by proximity and process payments automatically. Websites and ad tech platforms serve customers with highly personalized pages and ad content in real time. Natural language programming gives chatbots the ability to interpret and respond to natural language queries.
4. Smart Product Location
Applying algorithms to a retailer’s historical data for categories such as product location, customer preferences, seasonal sales, and external factors like weather and shipping costs, businesses can use AI to optimize inventory location across warehouses, brick-and-mortar stores, and display placement in stores.
Distributing products to optimal warehouse locations cuts storage and shipping costs, while reducing the chances that stores will sell out of high-demand products faster than regional resupplies can adjust. In turn, having the right products on hand and displayed in intuitive locations drives customer satisfaction and increases the likelihood customers will return to a particular location.
5. Workforce Planning
Maintaining adequate staffing levels through seasonal and economic change is a perennial challenge in retail. Understaffing leads to unsatisfactory customer experiences and employee burnout, while overstaffing runs up training and provisioning costs and leaves many employees with fewer hours than they need to work.
With AI-driven analytics for regional, seasonal, and economic trends, retailers can establish data-backed staffing quotas for stores, warehouses, and drivers. Additionally, real-time data monitoring helps businesses make quick adjustments when economic conditions change unexpectedly.

6. Price Optimization
Pricing is another critical retail task traditionally fraught with speculation and guesswork. While businesses have long practiced pricing strategies based on competitor pricing, historical sales data, or supply-and-demand dynamics, the ability to analyze data in significant depth across multiple categories has only become possible through recent developments in AI.
AI now enables businesses to run multiple complex pricing strategies simultaneously, while supplying deeper analytics for each strategy. For example, applying AI to customer data allows businesses to identify key-value items – products exhibiting high popularity with price-conscious customers. Lowering prices on these products drives customer satisfaction for regularly purchased items while letting businesses recoup losses with distributed price raises on other products.
Combining data for key-value items with other real-time analytics, such as dynamic pricing, to match or undercut competitors would be an impossibility for businesses using manually written queries. However, for AI, factoring in multiple variables from live data doesn’t require a significant increase in time or resources.
7. Heightened Security and Loss Prevention
Today’s AI-powered video analytics software can monitor and flag potentially significant human behaviors, such as unusual hand movements or rapid changes in pace, with greater reliability than trained human observers. Adopting this technology helps businesses prevent losses more effectively while reducing the need for monotonous camera monitoring by security staff.
In this video, you’ll see some examples of how retailers use AI:
Pricing and Inventory AI for Profit Optimization with Hypersonix
To compete in today’s unforgiving marketspace, businesses must develop capabilities for real-time data analytics at scale. Hypersonix’s AI platform enables powerful business intelligence for retailers and ecommerce companies. With Hypersonix, decision-makers get the advantage of deep insights extracted from thousands of simulations and AI-generated recommendations.
To learn more and schedule a demo, contact Hypersonix.
.png)

-1.png)


